What Exactly Is the Dark Web?
Most people use the internet every day without realizing they’re only skimming the surface. Open Google, scroll Instagram, check emails—that’s the visible layer of the web. Beneath it lies an enormous portion of the internet that isn’t indexed by search engines. That hidden space is often confused with the Dark Web, but the reality is more structured.
The internet can be divided into three main layers: the Surface Web, the Deep Web, and the Dark Web. Each serves a different purpose, and understanding them clears up a lot of myths.
Surface Web, Deep Web, and Dark Web: The Layers of the Internet
Surface Web
This is the part of the internet everyone knows. Search engines like Google and Bing crawl these pages, making them easy to access. News sites, social media, blogs, online shops, YouTube—this is all surface-level content. Estimates suggest it makes up less than 5% of the entire internet.
Deep Web
The Deep Web is where the majority of online information lives. It isn’t indexed by search engines because it sits behind logins or paywalls. Think of your email inbox, bank account, private databases, subscription services, medical records, or university portals. These aren’t shady; they’re just not open to public crawling. In fact, the Deep Web is essential for privacy and security.
Dark Web
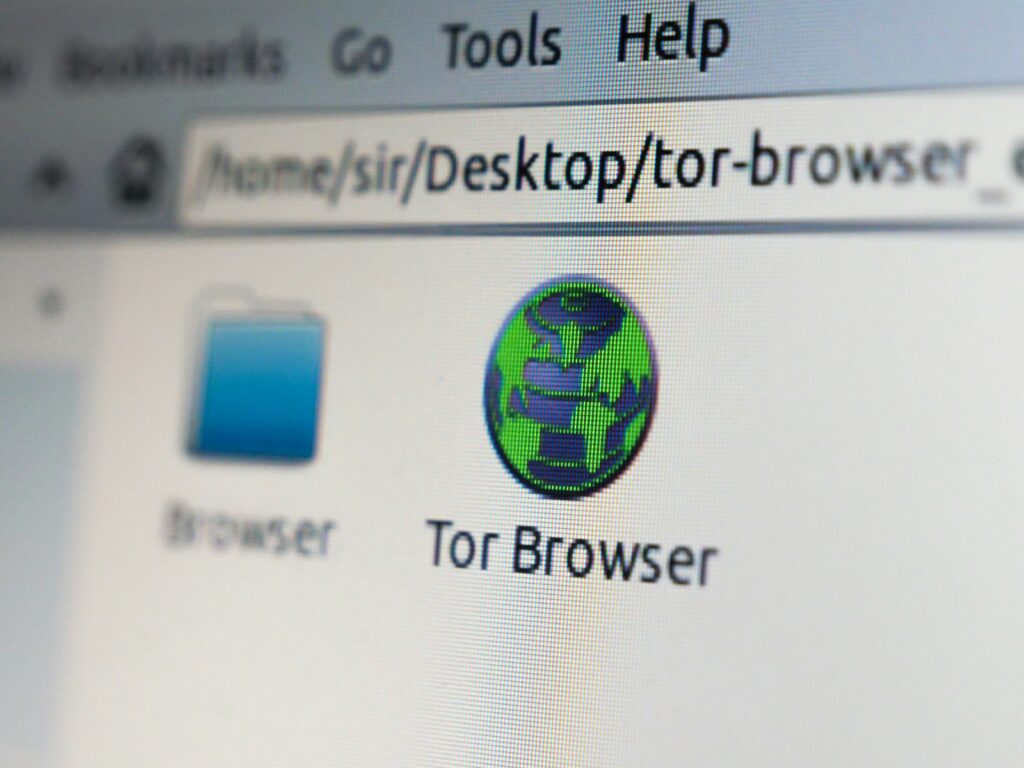
The Dark Web is a small portion of the Deep Web, but it’s intentionally hidden. Sites on the Dark Web don’t use standard domains like .com or .org. Instead, they use .onion domains, which require special software like the Tor Browser to access. These websites don’t appear in Google results and often rely on encrypted, anonymous networks.
While the Dark Web is infamous for hosting illegal activities, it isn’t entirely criminal. It also supports privacy-focused communities, secure communication platforms, and whistleblowing sites.
Access https://www.torproject.org/
Why the Dark Web Exists
The Dark Web wasn’t created as a criminal playground. Its foundation comes from the need for privacy, anonymity, and freedom of information. Governments, researchers, journalists, and activists have used hidden networks for decades to bypass censorship and protect sensitive communication.
For example, the Tor Project—originally developed with support from the U.S. Naval Research Lab—was designed to allow intelligence sources to communicate securely. Over time, it became a tool for anyone who values anonymity online.
Pubg Lite New https://marklure.com/pubg-mobile-lite-2025-last-update-shutdown-return/
Today, the Dark Web serves multiple purposes:
- Censorship resistance: In countries where internet access is tightly controlled, the Dark Web offers citizens a way to communicate freely.
- Whistleblowing and activism: Platforms like SecureDrop allow insiders to leak documents safely.
- Privacy: Some users simply don’t want corporations, governments, or hackers tracking their online activities.
Of course, alongside these legitimate uses, the Dark Web has also become notorious for black markets, hacking forums, and other illegal services. That dual nature is what makes it both fascinating and controversial.
How the Dark Web Works in 2025

The Dark Web isn’t a separate internet. It’s a network that runs on top of the existing infrastructure but relies on different rules of access and anonymity. You can’t reach it with Chrome or Safari. You need specific tools that protect your identity and connect you to hidden domains.
At the center of this ecosystem is Tor, short for The Onion Router.
The Role of Tor and Onion Routing
Tor is free, open-source software that enables anonymous browsing. When you use Tor, your internet traffic doesn’t move directly from your device to a website. Instead, it bounces through multiple servers, or “nodes,” around the world. Each relay peels off one layer of encryption—like an onion—until the request reaches its destination.
This process makes it extremely difficult for anyone to trace who is accessing a site or where a site is hosted. That’s why Tor is both a tool for privacy advocates and a magnet for criminals.
While Tor is the most popular gateway, it’s not the only one. Other networks like I2P and Freenet also exist, though they’re smaller and less mainstream. Still, Tor remains the backbone of the Dark Web in 2025.
Hidden Websites and .onion Domains
Websites on the Dark Web don’t use standard top-level domains like .com or .org. Instead, they operate with .onion addresses. These are long, complex strings of characters that look nothing like traditional URLs.
Example:http://3g2upl4pq6kufc4m.onion
That address belongs to DuckDuckGo’s Dark Web search engine. Unlike Google, it doesn’t log your data or track your searches.
Most .onion websites are not easy to find. You usually need direct links, directories, or community recommendations. Search engines exist on the Dark Web, but they’re limited and sometimes unreliable. This scarcity of indexing is deliberate—it protects anonymity but also makes navigation tricky.
What You Can Actually Find on the Dark Web

The popular image of the Dark Web often focuses on illegal markets selling drugs, weapons, or stolen credit cards. Those things are real, but they don’t represent the entire ecosystem. In 2025, you’ll encounter a mix of communities and services:
- Marketplaces: Some are legitimate, selling privacy tools or encrypted hosting. Others are illegal, offering counterfeit goods, malware, or hacking-for-hire services.
- Forums and communities: Privacy advocates, hackers, journalists, and researchers often gather in discussion boards hidden from the Surface Web.
- Libraries and archives: You can find large collections of books, research papers, and restricted documents. Some are perfectly legal, while others may contain pirated or banned material.
- Whistleblowing platforms: SecureDrop and GlobaLeaks provide safe channels for insiders to share sensitive information with journalists.
- Communication services: Encrypted email providers and chat platforms thrive in this environment, giving users alternatives to mainstream messaging apps.
- Search engines: Tools like DuckDuckGo’s onion version or Ahmia help users navigate, though they only cover a fraction of sites.
It’s important to note that not everything on the Dark Web is functional or trustworthy. Many sites disappear overnight. Some exist only to scam newcomers. Others are honey pots, set up by law enforcement to monitor activity.
In short, the Dark Web is less like a single hidden world and more like a patchwork of secret rooms. Some are valuable and safe, while others are dangerous traps. The challenge is knowing the difference.
Dark Web vs Deep Web: Key Differences
Many people mix up the Deep Web and the Dark Web. The distinction matters.
GTA 6 News https://marklure.com/gta-6-release-date-gameplay-map/
The Deep Web is simply anything not indexed by search engines. That includes your Gmail inbox, private Facebook messages, cloud storage, medical records, or Netflix’s internal database. None of these are illegal—they’re just protected by logins or firewalls. Without the Deep Web, modern life wouldn’t function.
The Dark Web, on the other hand, is a small slice of the Deep Web that’s intentionally hidden and requires special tools like Tor to access. Instead of being private by necessity (like a password-protected account), Dark Web sites are private by design. Their creators don’t want them discovered by the general public.
To simplify:
- Deep Web = ordinary hidden data (banking, email, subscriptions).
- Dark Web = intentionally concealed networks, often anonymous and encrypted.
Myths and Misconceptions About the Dark Web
Because the term “Dark Web” sounds ominous, a lot of myths circulate around it. Let’s clear a few of the most common:
Myth 1: Everything on the Dark Web is illegal.
Not true. While illegal trade exists, so do legal communities, academic resources, privacy tools, and whistleblower platforms.
Myth 2: Accessing the Dark Web will instantly put you on a government watchlist.
Simply opening the Tor browser or visiting a .onion site isn’t illegal in most countries. What you do there determines the legal risk.
Myth 3: The Dark Web is massive compared to the Surface Web.
It’s actually much smaller than people imagine. The Deep Web is huge, but the Dark Web itself is only a fraction of that.
Myth 4: Hackers will immediately steal your data.
There are risks, but just visiting the Dark Web doesn’t guarantee compromise. Problems usually arise when users download files, click malicious links, or engage in shady transactions.
Myth 5: Only criminals use the Dark Web.
Activists, journalists, researchers, and even everyday citizens use it to protect privacy. The Dark Web is a tool. How it’s used depends on the person.
Privacy Realeted https://www.privacytools.io/
The Legal Side: Is Accessing the Dark Web Illegal?
The question most beginners ask is simple: “Will I get in trouble if I open the Dark Web?”
The answer depends on what you do there. In most democratic countries, merely accessing the Dark Web is not illegal. Downloading the Tor browser, visiting .onion sites, or reading forums doesn’t break the law. After all, Tor itself is an open-source privacy tool supported by organizations and even government funding.
Where you run into legal issues is when you participate in criminal activity. Buying drugs, weapons, counterfeit documents, or stolen data is illegal regardless of the platform. Engaging in hacking-for-hire or distributing malicious software is also a crime.
Some countries with strict internet censorship laws do punish Tor usage itself. In places like China or North Korea, accessing the Dark Web can attract government attention. That’s why many users combine Tor with a VPN for extra protection.
Law enforcement agencies worldwide actively monitor Dark Web markets and forums. High-profile takedowns, such as Silk Road and AlphaBay, prove that anonymity doesn’t guarantee safety. Transactions leave trails, and undercover operations are common.
So the rule is straightforward: looking around is legal, but participating in crime isn’t.
More Info https://www.europol.europa.eu/
In short, the Dark Web isn’t a forbidden zone by default. It’s a tool. Like any tool, its legality depends on how you use it.
What Really Happens on the Dark Web
The Dark Web is often painted as a lawless underworld, but the reality is more layered. Yes, illegal trade exists, but so do communities and platforms with legitimate purposes. To understand it fully, you need to see both sides.
Illegal Activities

Black markets are the most notorious part of the Dark Web. They operate like e-commerce sites but trade in restricted goods. The most common include:
- Drugs: From cannabis to synthetic opioids, these markets often mimic Amazon-style layouts, complete with ratings and reviews.
- Weapons: Firearms and explosives occasionally appear, though most large-scale listings are scams.
- Stolen data: Hacked credit card numbers, login credentials, and identity documents are frequently sold.
- Counterfeit goods: Fake passports, driver’s licenses, and even university degrees circulate through certain vendors.
- Hacking services: Some sites offer malware, ransomware kits, or even “hacking for hire.” Many of these are traps designed to scam newcomers.
Law enforcement agencies constantly infiltrate and shut down major marketplaces. Silk Road, AlphaBay, and Wall Street Market were once dominant players, but their collapse shows how unstable these platforms can be. New markets spring up, but their lifespan is often short.
Legitimate Uses
Despite the illegal trade, not everything is criminal. The Dark Web also serves as a platform for people who need privacy and protection:
- Journalists and whistleblowers: Platforms like SecureDrop allow insiders to leak documents without exposing their identity. Major media organizations use it to protect sources.
- Political activists: In countries with heavy censorship, the Dark Web provides a space to organize, communicate, and share banned information.
- Privacy enthusiasts: Some users simply don’t want corporations tracking every click. They use the Dark Web for email, messaging, or file sharing with stronger anonymity.
- Educational resources: Hidden libraries host rare books, banned publications, and research archives not easily found on the open internet.
These uses highlight that the Dark Web isn’t inherently evil—it’s a tool that can be wielded for both good and bad.
Dangers of the Dark Web in 2025

While it has legitimate purposes, exploring the Dark Web isn’t without risks. The anonymity that protects users also creates opportunities for fraud and exploitation.
Malware and Scams
Malware is a constant threat. Many files shared on the Dark Web are laced with trojans or spyware designed to steal data. Downloading software or clicking on suspicious links can infect your system in seconds.
Scams are even more common. Fake vendors often set up shop, take payment, and vanish. Because transactions usually involve cryptocurrency, recovering funds is almost impossible. Even supposedly reputable sellers can run “exit scams,” where they suddenly disappear with customer deposits.
Data Breaches and Identity Theft
Hacked databases often end up for sale on Dark Web forums. Email accounts, phone numbers, and social security details circulate in bulk. Criminals buy this data to run phishing attacks, open fraudulent accounts, or drain financial assets.
For ordinary users, this means that your information could already be on the Dark Web without your knowledge. Services like Have I Been Pwned let you check if your email has appeared in leaked datasets.
Fake Marketplaces and Honey Pots
Not every site on the Dark Web is what it seems. Some are set up by scammers, while others are run by law enforcement as traps to catch criminals. To an inexperienced visitor, distinguishing between a real community and a setup can be almost impossible.
Even experienced users often treat every interaction with caution. Trust is scarce, and paranoia is part of survival.
In short, the Dark Web offers both freedom and danger. It enables privacy but also exposes you to serious risks if you’re careless. For beginners, the line between curiosity and catastrophe can be very thin.
How to Access the Dark Web Safely
Curiosity drives many people toward the Dark Web, but diving in without preparation is risky. If you’re determined to look around, safety should be your top priority.
Essential Tools
- Tor Browser: The primary gateway. Download it only from the official Tor Project site to avoid malicious versions.
- VPN: While Tor hides your traffic within its network, using a VPN adds another protective layer, shielding your activity from internet service providers and giving you an extra layer of anonymity.
- Security software: Antivirus and anti-malware programs are necessary. Even browsing can expose you to harmful files.
Security Practices You Can’t Ignore
- Never use your real identity. Don’t log into personal accounts, share personal details, or use real emails.
- Stick to trusted sources. Rely on well-known directories or recommendations from credible communities. Many random links are scams or malware traps.
- Avoid downloads. Files are the fastest way to infect your system. Unless you know exactly what you’re opening, skip it.
- Use cryptocurrency with caution. Bitcoin and Monero are common for transactions, but even those aren’t foolproof. Every transaction leaves a trace.
- Expect nothing to be permanent. Sites vanish overnight. Communities shift constantly. If you find something useful, assume it may not be there tomorrow.
The safest strategy for most beginners is to explore only informational or community-driven areas. If you’re tempted to buy or sell, understand that you’re stepping into dangerous territory both legally and financially.
Why Most People Should Stay Away
While accessing the Dark Web isn’t illegal in most countries, the dangers outweigh the benefits for casual users. The reality is that 95% of what the average person seeks—privacy tools, uncensored news, or secure messaging—can often be found through safer, legal alternatives.
Unless you have a specific need, there’s little reason to dive deep. Curiosity is natural, but reckless exploration can cost you data, money, or worse.
The Future of the Dark Web
The Dark Web in 2025 looks different than it did a decade ago. It’s evolving with technology and facing increasing pressure from governments and corporations.
AI and Cybercrime
Artificial intelligence is reshaping cybercrime. Automated phishing campaigns, AI-generated malware, and deepfake scams are now common on underground forums. At the same time, AI tools are also used by law enforcement to track suspicious activity more efficiently.
Governments Monitoring the Dark Web
Authorities worldwide are investing heavily in surveillance. Operations by Europol, the FBI, and Interpol regularly dismantle markets and arrest high-profile figures. Even if users feel anonymous, law enforcement often has the patience and resources to trace transactions over time.
The Rise of Privacy-Driven Communities
Despite crackdowns, demand for privacy isn’t disappearing. Encrypted chat platforms, decentralized marketplaces, and anonymous hosting providers continue to grow. Many users aren’t criminals—they’re people tired of constant tracking, advertising, and surveillance on the Surface Web.
The Dark Web may shrink in size due to pressure, but it won’t vanish. As long as people value privacy and secrecy, hidden networks will find a way to exist.
Should You Explore the Dark Web?
The Dark Web is both fascinating and dangerous. It holds communities fighting for free speech and privacy, but it also harbors scams, stolen data, and criminal trade. For beginners, the key is perspective: this isn’t a magical hidden internet—it’s a niche layer with specific purposes, some good, some bad.
If your interest is purely educational, reading guides and following cybersecurity experts will give you more value than actually diving in. If you do decide to explore, use the right tools, take precautions, and never assume you’re untouchable.
At the end of the day, the Dark Web is a reminder of what the internet could be without rules or oversight—freedom and danger wrapped together. Approach it with respect, skepticism, and caution.




This is quite the onion! Peel back the layers, and you find the Dark Web isnt just a shadowy place for illicit trade—oh no, its full of legitimate forums, hidden libraries, and even places for people who just *really* hate their internet provider knowing their search history. Its fascinating how a tool for privacy can be both a digital safe haven and a hunting ground for scammers, much like the Surface Webs own treasure trove of phishing attempts. The key takeaway seems to be: if youre not careful, you might end up in a less-than-safe room. Proceed with caution, or risk joining a data breach statistics chart!app đếm ngược ngày sinh nhật
This Deep Dive into the Dark Web is wonderfully onion-scented! It’s amusing how everyone thinks the Dark Web is just one giant bazaar for illicit goods, but really, it’s like the internet’s secret library and community center mixed with a slightly sketchy flea market. Who knew journalists and activists used it too? Still, the part about honey pots and malware feels like a warning label on a chocolate bar: May contain nuts… and undercover cops. Great read, though I’d advise everyone to bring a strong cup of paranoia and a healthy dose of skepticism!速度之星 多人模式
This is quite the onion of an article, isnt it? It lays out the layers of the Dark Web, from its encrypted pathways using Tor to the various .onion realms. While it’s funny to imagine the stereotype of drug dealers lurking around every corner, the article cleverly shows its just one small part of this hidden network, like a poorly indexed library mixed with a few dangerous traps. Calling it a patchwork of secret rooms is spot on – some are treasure chests of information, others just dark closets waiting to trip you up. The myth-busting about legality was a good laugh, proving its not a instant guilty verdict just for exploring. It’s a fascinating look at the shadowy side of the net, reminding us that with great privacy comes great… caution